AI Etüt Oturumu
Oturum Bilgileri
AI Öğretmen Değerlendirmesi
Tespit Edilen Eksikler
- Introduction to Functions and Linear Functions
- 2.1.a. Formal Definitions of Functions
Detaylı Değerlendirme
Öğrenci Performans Analizi
Bu derste öğrencinin "Fonksiyonlar ve Doğrusal Fonksiyonlara Giriş" konusundaki temel kavramları anlama düzeyi değerlendirilmiştir. Öğrenci, dersin genelinde konuya ilgili ve katılımcı bir tutum sergilemiştir. Bazı temel kavramları doğru anlarken, spesifik bir alanda belirgin bir kavram yanılgısı göstermiştir.
# Başarılı Olduğu Konular
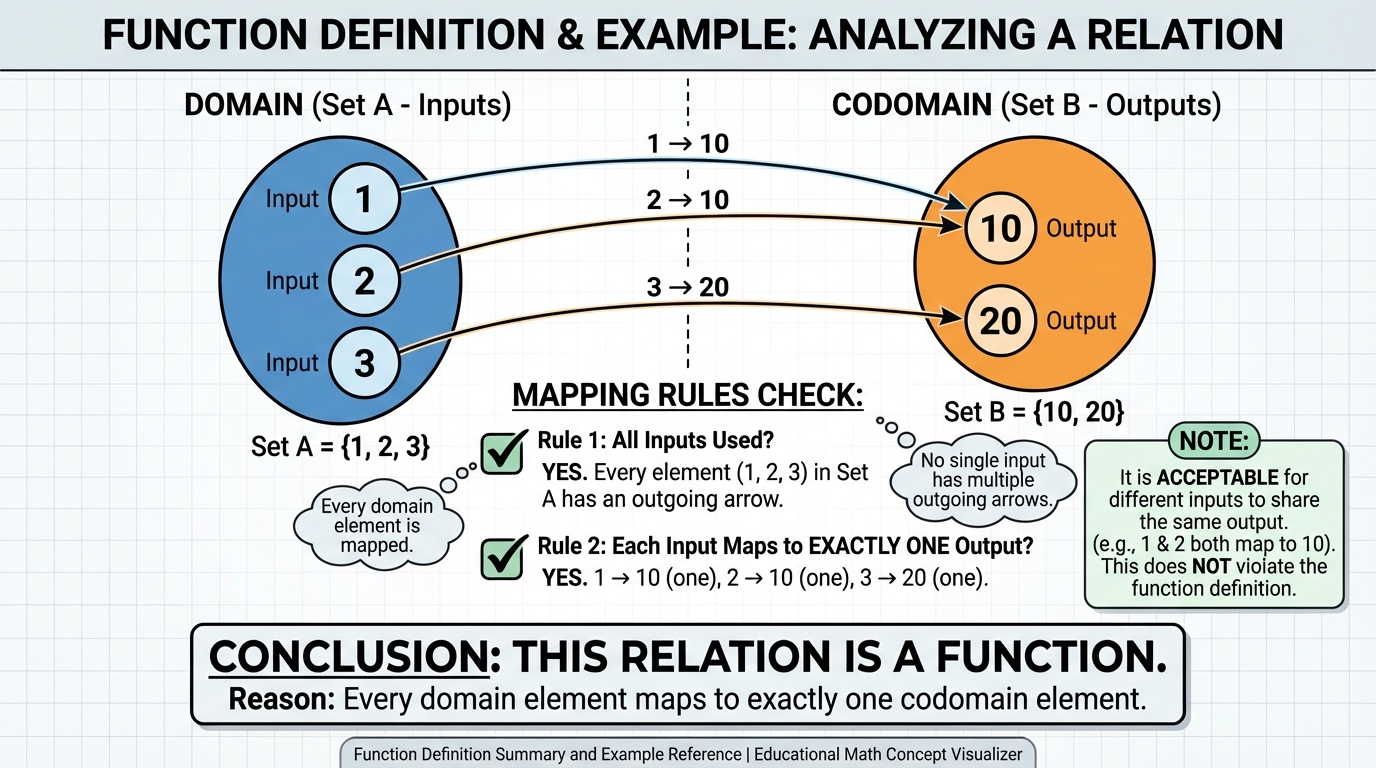
Öğrenci, fonksiyon tanımının temel mantığını, tanım ve değer kümelerinin fonksiyon olup olmama durumunu nasıl etkilediğini ve fonksiyonlarda değer bulmayı başarılı bir şekilde kavramıştır.
* Fonksiyon Tanımı: Bir ifadenin fonksiyon olabilmesi için tanım kümesindeki her elemanın değer kümesinde yalnızca bir karşılığı olması gerektiğini doğru bir şekilde anlamıştır. Özellikle, doğal sayılardan doğal sayılara tanımlı olmayan `f(x) = x - 3` fonksiyonu hakkındaki soruyu doğru bir mantıkla açıklamıştır.
* Tanım Kümesi Bulma: Rasyonel bir fonksiyonun en geniş tanım kümesini bulma sorusunda, paydayı sıfır yapan değeri bularak doğru cevaba ulaşmıştır. Bu, fonksiyonların tanım aralıkları üzerindeki kısıtlamaları anladığını göstermektedir.
* Fonksiyonda Değer Bulma: `f(x-1)` şeklinde verilen bir fonksiyonda `f(3)` değerini bulma sorusunu doğru çözmüştür. Bu, fonksiyonel ifadelerle işlem yapma becerisinin yerinde olduğunu göstermektedir.
# Geliştirilmesi Gereken Konular
Öğrencinin en belirgin eksikliği, bir fonksiyonun temel bileşenlerinden biri olan "Görüntü Kümesi" (Range) kavramını anlamada ortaya çıkmıştır.
* Tanım, Değer ve Görüntü Kümesi Ayrımı: Dersteki ilk soruda, şema ile verilen bir fonksiyonun tanım ve değer kümelerini doğru bir şekilde belirlemesine rağmen, görüntü kümesini yanlış tespit etmiştir. Görüntü kümesine, tanım kümesinden elemanlar ve değer kümesinde eşleşmemiş elemanlar dahil etmiştir. Bu durum, görüntü kümesinin "tanım kümesindeki elemanların eşleştiği gerçek çıktılar" olduğu bilgisinin tam olarak oturmadığını göstermektedir. Bu konunun tekrar edilmesi ve pekiştirilmesi gerekmektedir.
# Ders Dışı Yorumlar
Öğrencinin ders dışı herhangi bir yorumu veya sorusu olmamıştır.